Role of microRNAs in insect biology and host-pathogen interactions
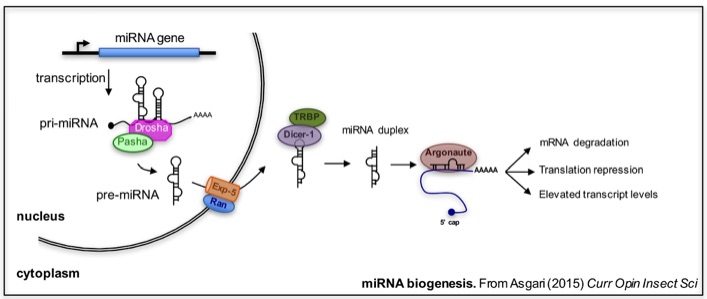
Small non-coding microRNAs (miRNAs; about 22 nucleotides), are increasingly recognized as important regulatory factors exerting strong control over many biological processes including development, cancer, immunity, longevity, and viral infections. In addition, miRNAs are likely to regulate host defence responses to pathogens. Tightly regulated proteins involved in these responses are presumably part of the pathogen detection network such as pattern recognition molecules or direct defence proteins such as anti-microbial peptides. We are focusing on determining the impact of pathogens on the hosts miRNA profile and investigate the role of differentially expressed miRNAs in host-pathogen interactions and insect development. This may lead to designing novel strategies to control insect pests or limit transmission of arboviruses.
Wolbachia-mosquito interactions
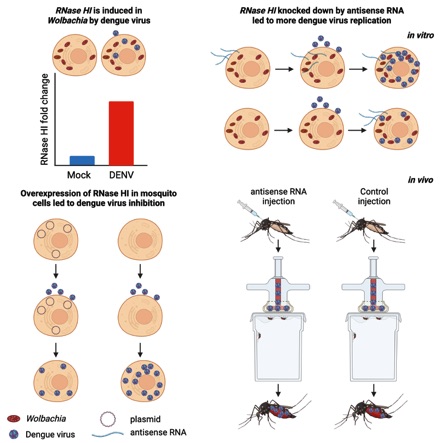
Wolbachia is a common endosymbiont in insects mostly known for reproductive manipulations of the host. In addition, Wolbachia blocks replication of several RNA viruses and some other vector-borne pathogens (Plasmodium) in insects. We are interested in exploring the role of miRNAs in Wolbachia-mosquito-virus interactions. We have shown that Wolbachia causes differential expression of a number of mosquito miRNAs and some are involved in Wolbachia maintenance in host cells. Further, we have developed a method to silence Wolbachia genes within the host cell that allows studying their role in Wolbachia's interactions with the host cell and in virus blocking. For example, Wolbachia RNase HI is induced in mosquito cells shortly after dengue virus infection that contributes to degrading viral RNA. Silencing the Wolbachia gene in cell culture and mosquitoes led to increased dengue virus replication suggesting the gene is involved in virus blocking (iScience 2023 26, 105836).
1) Exploring the role of cellular miRNAs in Wolbachia-mosquito interaction
2) Investigating the role of miRNAs in mosquito-virus interaction
3) Role of miRNAs and RNA interference in baculovirus-host interaction
4) Differential regulation of insect miRNAs in response to infection
5) miRNA biology in insects
Available student projects